Lazarus - OpenGL 3.3 Tutorial - Material Eigenschaften - Material Spot Light
Aus DGL Wiki
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Material Eigenschaften - Material Spot Light
Einleitung
Material-Eigenschaften sind auch mit Spot-Light möglich.
Dies funktioniert etwa gleich, wie das Point-Light ohne Material-Eigenschaften.
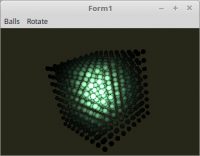
Bei diesem Beispiel, wird mit einer Taschenlampe in einen Jade-Würfel gezündet.
Dieser Shader ist schon sehr komplex.
Neben der Spotlichtberechnung, wird noch die Abschwächung des Lichtes berücksichtigt.
Vertex-Shader:
#version 330
layout (location = 0) in vec3 inPos; // Vertex-Koordinaten
layout (location = 1) in vec3 inNormal; // Normale
// Daten für Fragment-shader
out Data {
vec3 Pos;
vec3 Normal;
} DataOut;
// Matrix des Modeles, ohne Frustum-Beeinflussung.
uniform mat4 ModelMatrix;
// Matrix für die Drehbewegung und Frustum.
uniform mat4 Matrix;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = Matrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0);
DataOut.Normal = mat3(ModelMatrix) * inNormal;
DataOut.Pos = (ModelMatrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0)).xyz;
}
Fragment-Shader
#version 330
#define PI 3.1415
// === Licht
#define Lposition vec3(0.0, 0.0, 100.0)
#define Lambient vec3(1.8, 1.8, 1.8)
#define Ldiffuse vec3(1000.0, 1000.0, 1000.0)
// === Material ( Jade )
#define Mambient vec3(0.14, 0.22, 0.16)
#define Mdiffuse vec3(0.54, 0.89, 0.63)
#define Mspecular vec3(0.32, 0.32, 0.32)
#define Mshininess 12.8
// === Spotlicht Parameter
// Öffnungswinkel der Lampe
// 22.5°
#define Cutoff cos(PI / 2 / 4)
// Lichtrichtung, brennt senkrecht in der Z-Achse.
#define spotDirection vec3(0.0, 0.0, -1.0)
// === Für Abschwächung
// default 0.0
#define spotExponent 50.0
// Diese Werte entsprechen Attenuation Parametern vom alten OpenGL.
// default 1.0
#define spotAttConst 1.0
// default 0.0
#define spotAttLinear 0.0
// default 0.0
#define spotAttQuad 0.1
// Daten vom Vertex-Shader
in Data {
vec3 Pos;
vec3 Normal;
} DataIn;
out vec4 outColor;
// Abschwächung, abhängig vom Radius des Lichtes.
float ConeAtt(vec3 LightPos) {
vec3 lightDirection = normalize(DataIn.Pos - LightPos);
float D = length(LightPos - DataIn.Pos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (spotAttConst + spotAttLinear * D + spotAttQuad * D * D);
float angle = dot(spotDirection, lightDirection);
angle = clamp(angle, 0.0, 1.0);
if(angle > Cutoff) {
return attenuation;
} else {
return 0.0;
}
}
// Abschwächung anhängig der Lichtentfernung zum Mesh.
float ConeExp(vec3 LightPos) {
vec3 lightDirection = normalize(DataIn.Pos - LightPos);
float angle = dot(spotDirection, lightDirection);
angle = clamp(angle, 0.0, 1.0);
if(angle > Cutoff) {
return pow(angle, spotExponent);
} else {
return 0.0;
}
}
// Lichtstärke und Material anhand der Normale.
vec3 Light(in vec3 p, in vec3 n) {
vec3 nn = normalize(n);
vec3 np = normalize(p);
vec3 diffuse; // Licht
vec3 specular; // Reflektion
float angele = max(dot(nn, np), 0.0);
if (angele > 0.0) {
vec3 eye = normalize(np + vec3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0));
specular = pow(max(dot(eye, nn), 0.0), Mshininess) * Mspecular;
diffuse = angele * Mdiffuse * Ldiffuse;
} else {
specular = vec3(0.0);
diffuse = vec3(0.0);
}
return (Mambient * Lambient) + diffuse + specular;
}
void main(void) {
float c = ConeAtt(Lposition) * ConeExp(Lposition); // Beide Abschwächungen multipizieren.
outColor = vec4(vec3(c) * Light(Lposition - DataIn.Pos, DataIn.Normal), 1.0);
}
Autor: Mathias
Siehe auch
- Übersichtseite Lazarus - OpenGL 3.3 Tutorial