Lazarus - OpenGL 3.3 Tutorial - Beleuchtung - Spot Light, Abschwaechen
Aus DGL Wiki
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Beleuchtung - Spot Light, Abschwaechen
Einleitung
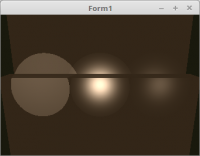
Wen das Licht schwächer wird, je weiter es von der Mesh entfernt wird, sieht es viel realistischer aus.
Auch wird ein Lichtstrahl schwächer je weit er vom Zentrum weg ist.
Die beiden linken Lichter wird nur eine Abschwächung angewendet. Das rechte Licht ist eine Kombination aus beiden Abschwächungen und somit die realistischte.
Dies Distanzabhängige Abschwächung, kann man auch bei einer Punkt-Beleuchtung anwenden.
Hier werden die Lichtpositionen der drei Lampen festgelegt.
procedure TForm1.CreateScene;
const
LichtPositionRadius = 25.0;
begin
with LightPos do begin
Red := vec3(-1.2, 0.0, 4.0);
Red.Scale(LichtPositionRadius);
Green := vec3(0.0, 0.0, 4.0);
Green.Scale(LichtPositionRadius);
Blue := vec3(1.2, 0.0, 4.0);
Blue.Scale(LichtPositionRadius);
end;
Hier werden die 3 Lichter in der Z-Achse bewegt.
procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
const
Step: single = 0.5;
min = 40.0;
max = 80.0;
ZPos: single = (max + min) / 2;
begin
ModelMatrix.Identity;
ModelMatrix.Translate(0.0, 0.0, 30);
ModelMatrix.RotateA(0.25);
ZPos += Step;
if (ZPos > max) or (ZPos < min) then begin
Step *= -1;
end;
LightPos.Red.z := ZPos;
ZPos += Step;
if (ZPos > max) or (ZPos < min) then begin
Step *= -1;
end;
LightPos.Green.z := ZPos;
ZPos += Step;
if (ZPos > max) or (ZPos < min) then begin
Step *= -1;
end;
LightPos.Blue.z := ZPos;
ogc.Invalidate;
end;
Berechnen der 3 Lichtkegel.
Vertex-Shader:
#version 330
layout (location = 0) in vec3 inPos; // Vertex-Koordinaten
layout (location = 1) in vec3 inNormal; // Normale
out Data {
vec3 pos;
vec3 Normal;
} DataOut;
uniform mat4 ModelMatrix;
uniform mat4 Matrix; // Matrix für die Drehbewegung und Frustum.
void main(void) {
gl_Position = Matrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0);
DataOut.Normal = mat3(ModelMatrix) * inNormal;
DataOut.pos = (ModelMatrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0)).xyz;
}
Fragment-Shader
#version 330
#define PI 3.1415
// Eine leichte Hintergrundbeleuchtung.
#define ambient vec3(0.2, 0.15, 0.095)
// Farbe des Lichtstrahles.
#define yellow vec3(1.0, 0.9, 0.8)
// Öffnungswinkel der Lampe
// 22.5°
#define Cutoff cos(PI / 2 / 4)
// Lichtrichtung, brennt senkrecht in der Z-Achse.
#define spotDirection vec3(0.0, 0.0, -1.0)
// Für Abschwächung
// default 0.0
#define spotExponent 50.0
// Diese Werte entsprechen Attenuation Parametern vom alten OpenGL.
// default 1.0
#define spotAttConst 1.0
// default 0.0
#define spotAttLinear 0.1
// default 0.0
#define spotAttQuad 0.0
in Data {
vec3 pos;
vec3 Normal;
} DataIn;
uniform vec3 LeftLightPos;
uniform vec3 CenterLightPos;
uniform vec3 RightLightPos;
out vec4 outColor; // ausgegebene Farbe
// Abschwächung, abhängig vom Radius des Lichtes.
float ConeAtt(vec3 LightPos) {
vec3 lightDirection = normalize(DataIn.pos - LightPos);
float D = length(LightPos - DataIn.pos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (spotAttConst + spotAttLinear * D + spotAttQuad * D * D);
float angle = dot(spotDirection, lightDirection);
angle = clamp(angle, 0.0, 1.0);
if(angle > Cutoff) {
return attenuation;
} else {
return 0.0;
}
}
// Abschwächung anhängig der Lichtentfernung zum Mesh.
float ConeExp(vec3 LightPos) {
vec3 lightDirection = normalize(DataIn.pos - LightPos);
float angle = dot(spotDirection, lightDirection);
angle = clamp(angle, 0.0, 1.0);
if(angle > Cutoff) {
return pow(angle, spotExponent);
} else {
return 0.0;
}
}
// Lichtstärke anhand der Normale.
float light(vec3 p, vec3 n) {
vec3 v1 = normalize(p);
vec3 v2 = normalize(n);
float d = dot(v1, v2);
return clamp(d, 0.0, 1.0);
}
void main(void) {
// Grundbeleuchtung
outColor = vec4(ambient, 1.0);
float c;
// Nur Attenuation ( Links )
c = ConeAtt(LeftLightPos);
outColor.rgb += vec3(c) * light(LeftLightPos - DataIn.pos, DataIn.Normal) * yellow;
// Nur Exponent ( Mitte )
c = ConeExp(CenterLightPos);
outColor.rgb += vec3(c) * light(CenterLightPos - DataIn.pos, DataIn.Normal) * yellow;
// Kombiniert ( Rechte )
float c1 = ConeAtt(RightLightPos);
float c2 = ConeExp(RightLightPos);
c = c1 * c2; // Beide Abschwächungen multipizieren.
outColor.rgb += vec3(c) * light(RightLightPos - DataIn.pos, DataIn.Normal) * yellow;
}
Autor: Mathias
Siehe auch
- Übersichtseite Lazarus - OpenGL 3.3 Tutorial